Introduction
Chest pain is a sensation that demands attention. Whether it’s a fleeting discomfort or a sharp, persistent ache, chest pain can be alarming and worrisome. In this blog, we will delve into the world of chest pain, exploring its definition, common causes, the intricate workings of its pathophysiology, recognizable symptoms, and the various treatment options available.
Table of Contents
Defining Chest Pain:
Chest pain is a sensation of discomfort or pain that occurs anywhere between the neck and the upper abdomen. It’s a complex sensation that can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from minor issues to serious medical conditions.
Exploring the Causes:
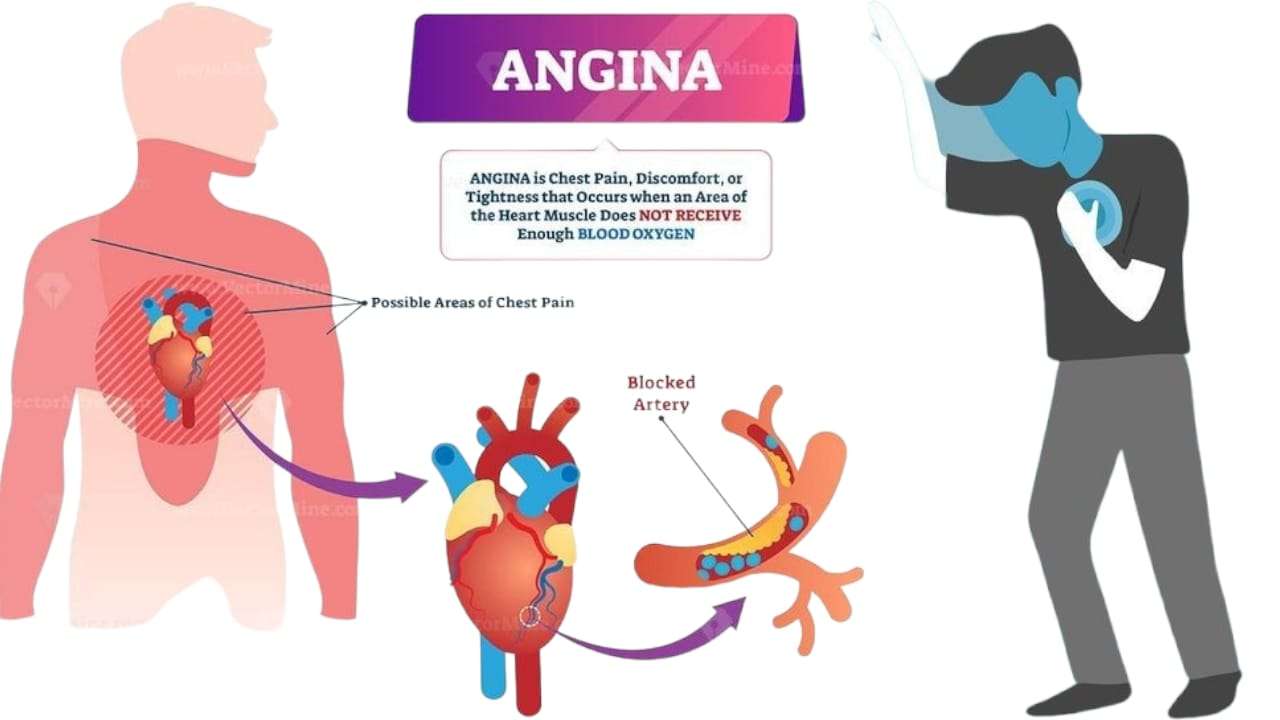
1. Heart-Related Causes: Chest pain can often be linked to heart-related problems, such as angina (which is a result of reduced blood flow to the heart) or a heart attack (when blood flow is completely blocked).
2. Musculoskeletal Causes: Issues with muscles, ribs, or joints in the chest area can also lead to chest pain. Conditions like costochondritis or muscle strain fall under this category.
3. Gastrointestinal Causes: Acid reflux, inflammation of the esophagus, or conditions like gallstones can cause chest pain that may mimic heart-related discomfort.
4. Respiratory Causes: Lung infections, inflammation, or conditions like pneumonia can lead to chest pain, especially when breathing deeply or coughing.
5. Anxiety and Panic Attacks: Emotional distress, anxiety, and panic attacks can trigger chest pain due to the physiological responses these conditions cause.

Simplified Pathophysiology :
Imagine your chest as a busy neighborhood with different parts working together. When something goes wrong, like a blocked road or a problem with the houses, you might feel pain. That’s what happens with chest pain – it’s like an alert that something isn’t right in your chest neighborhood.
1. Problem Signals:
Inside your chest, there are tiny parts called nerves. These nerves are like messengers that tell your brain about things happening in your chest. When something isn’t right – like not enough blood or inflammation – these nerves send signals to your brain, saying, “Hey, something’s not okay here!”
2. Brain Gets the Message:
When your brain receives these signals, it starts to figure out what’s wrong. It’s like your brain is a detective trying to solve a puzzle. It looks at the signals and tries to understand what’s causing the problem.
3. Sensation of Pain:
Once your brain figures out the issue, it might make you feel pain. It’s like your body’s way of saying, “Pay attention! Something’s going on!” The pain helps you know that there’s a problem that needs fixing.
4. Different Causes, Same Process:
Chest pain can happen for lots of reasons. Sometimes, it’s because the heart needs more blood, other times it’s because of muscle strain or inflammation. No matter the reason, the process of nerves sending signals to your brain is pretty similar.
5. Seeking Help:
If you feel chest pain, it’s important to tell an adult. They can help figure out if it’s something simple or if you need to see a doctor. Doctors can do tests to find out what’s causing the pain and how to make it better.
So, chest pain is like your body’s alarm system. It’s how your body lets you know that something’s not right in your chest neighborhood. Just like superheroes, your body’s nerves and brain work together to keep you safe and healthy!
Recognizing Symptoms:
Chest pain isn’t always the only symptom. It can be accompanied by shortness of breath, nausea, sweating, or pain radiating down the arm or jaw. The combination of symptoms can provide clues about the underlying cause.
Seeking Medical Attention:
Because chest pain can range from minor to life-threatening, it’s important to seek medical attention if you experience it. Your healthcare provider will assess your symptoms, medical history, and possibly perform tests like an electrocardiogram (ECG), blood tests, or imaging to determine the cause.
Treatment Options:
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the pain:
1. Heart-Related Issues: For heart-related causes, treatments may include medications to improve blood flow, lifestyle changes, and in severe cases, procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery.
2. Musculoskeletal and Respiratory Causes: Anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and rest can help alleviate pain caused by musculoskeletal or respiratory issues.
3. Gastrointestinal Causes: Dietary changes, antacids, and medications to reduce stomach acid can help manage chest pain due to gastrointestinal causes.
4. Anxiety and Panic Attacks: Counseling, stress management techniques, and, in some cases, medications can help address the underlying psychological causes of chest pain.