Definition
Contraception methods play a crucial role in preventing unwanted pregnancies and promoting safe and responsible sexual health practices. With a wide range of options available, it can be overwhelming to choose the right method that suits your individual needs and preferences. In this article, we will explore the different methods of contraception and their effectiveness, benefits, and considerations.
Table of Contents
1. Hormonal Methods of Contraception
Hormonal contraception methods such as birth control pills, patches, and injections work by altering hormone levels in the body to prevent ovulation. These methods are highly effective when used correctly and consistently. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable hormonal contraception method for you based on your medical history and lifestyle.
Types of Hormonal Contraception
Birth Control Pills: Also known as oral contraceptives, birth control pills are taken daily to prevent pregnancy. They contain synthetic hormones that mimic the natural hormones produced by a woman’s body.
Patches: Birth control patches are worn on the skin and release hormones into the bloodstream to prevent ovulation.
Injections: Hormonal injections are administered every few months and contain progestin, a synthetic hormone that prevents pregnancy by thickening the cervical mucus and thinning the lining of the uterus.
Implants: Hormonal implants are small rods that are inserted under the skin of the upper arm and release hormones into the bloodstream to prevent pregnancy for up to five years.

How Hormonal Contraception Works
Hormonal contraception works by preventing ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovaries), thickening the cervical mucus to prevent sperm from reaching the egg, and thinning the lining of the uterus to prevent a fertilized egg from implanting.
These methods are highly effective when used correctly, with birth control pills being up to 99% effective in preventing pregnancy. However, it is important to note that hormonal contraception does not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Potential Side Effects of Hormonal Contraception
While hormonal contraception is generally safe and well-tolerated by most women, some may experience side effects such as:
– Nausea
– Headaches
– Weight gain
– Mood changes
– Irregular bleeding
– Breast tenderness
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting hormonal contraception to discuss any potential risks and benefits.
2. Barrier Methods
Barrier methods of contraception, such as condoms and diaphragms, create a physical barrier that prevents sperm from reaching the egg. These methods not only protect against unwanted pregnancies but also provide protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is important to use barrier methods correctly and consistently to ensure maximum effectiveness.
Types of Barrier Methods
There are several types of barrier methods that can be used during sexual activity. The most common ones include:
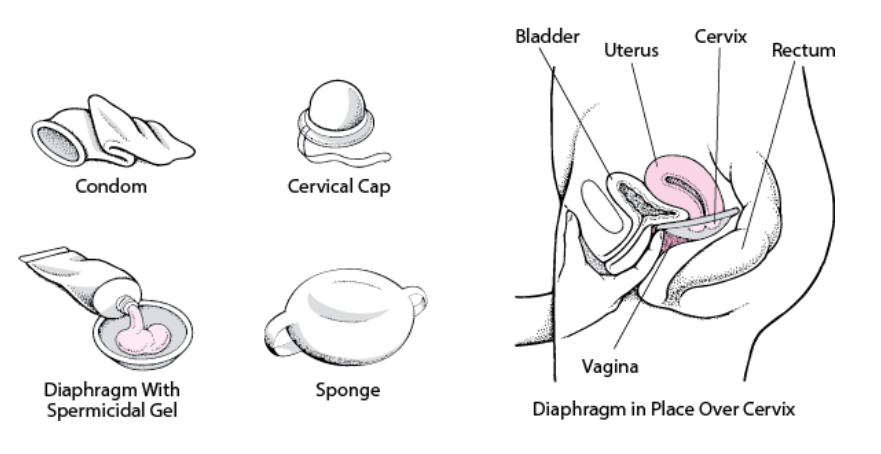
1. Condoms: Condoms are thin sheaths made of latex, polyurethane, or natural membranes that are worn over the penis or inserted into the vagina. They prevent the exchange of bodily fluids during intercourse, reducing the risk of STIs and pregnancy.
2. Diaphragms: Diaphragms are flexible, shallow cups made of silicone that are inserted into the vagina before intercourse. They cover the cervix and prevent sperm from entering the uterus.
3. Cervical caps: Cervical caps are similar to diaphragms but smaller in size. They fit snugly over the cervix and block sperm from entering the uterus.
4. Spermicides: Spermicides are chemical substances that come in the form of gels, foams, creams, or suppositories. They contain sperm-killing agents that immobilize sperm and prevent pregnancy.
How Barrier Methods Work
Barrier methods work by physically blocking sperm from reaching the egg or by killing sperm before they can fertilize an egg. Condoms, diaphragms, and cervical caps create a barrier that prevents sperm from entering the uterus, while spermicides immobilize sperm and stop them from swimming towards the egg. Sponges work by releasing spermicides and absorbing semen.
Effectiveness of Barrier Methods
Barrier methods are generally effective in preventing pregnancy when used correctly and consistently. Condoms, for example, have a success rate of around 98% when used properly. However, it is essential to note that barrier methods are not 100% effective and may fail in some cases. It is recommended to use barrier methods in combination with other forms of contraception for added protection.
3. Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
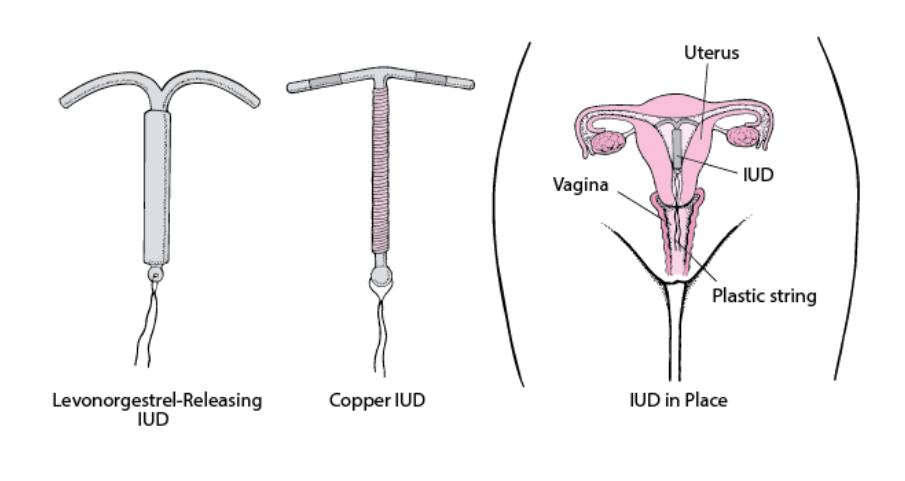
IUDs are small, T-shaped devices that are inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. There are two types of IUDs: hormonal and non-hormonal. Hormonal IUDs release hormones that prevent ovulation, while non-hormonal IUDs create an inflammatory reaction in the uterus that is toxic to sperm. IUDs are considered one of the most effective forms of contraception and can provide long-term protection for up to 5-10 years.
Types of Intrauterine Devices
When it comes to birth control options, intrauterine devices (IUDs) are becoming increasingly popular among women around the world. An IUD is a small, T-shaped device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. There are several different types of IUDs available, each with its own unique features and benefits. In this article, we will explore the various types of intrauterine devices and how they work to provide effective contraception.
Copper IUD
One of the most common types of IUDs is the copper IUD. This type of IUD is hormone-free and works by releasing copper ions into the uterus, which creates an inhospitable environment for sperm. The copper IUD can stay in place for up to 10 years and is highly effective at preventing pregnancy.
Hormonal IUD
Another popular type of IUD is the hormonal IUD, which releases a small amount of progestin hormone into the uterus. This hormone thickens the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg, and also thins the lining of the uterus, making it less likely for a fertilized egg to implant. Hormonal IUDs can stay in place for 3-5 years, depending on the type.
Levonorgestrel IUD
The levonorgestrel IUD is a specific type of hormonal IUD that releases the hormone levonorgestrel into the uterus. This type of IUD is highly effective at preventing pregnancy and can also be used to help manage heavy menstrual bleeding. The levonorgestrel IUD can stay in place for up to 5 years.
Silver IUD
The silver IUD is a newer type of IUD that contains silver nanoparticles, which have antimicrobial properties. This type of IUD is designed to reduce the risk of infection and inflammation in the uterus while providing effective contraception. The silver IUD can stay in place for up to 5 years.
Benefits of Intrauterine Devices
IUDs are highly effective at preventing pregnancy, with long-lasting protection that can range from 3 to 10 years, depending on the type of IUD. They are a convenient option for women who do not want to have to remember to take a daily pill or use other forms of birth control. IUDs are also reversible, meaning fertility returns quickly after removal.
Procedure for Inserting an IUD
Inserting an IUD is a simple procedure that can be done in a healthcare provider’s office. The cervix is gently dilated, and the IUD is inserted into the uterus through the cervix. The procedure may cause some discomfort, but it is usually well tolerated. Once inserted, the IUD can remain in place for several years.
Side Effects and Risks of Intrauterine Devices
While IUDs are safe and effective for most women, there are some risks and potential side effects to be aware of. Common side effects include irregular bleeding, cramping, and changes in menstrual flow. More serious risks, although rare, can include infection, perforation of the uterus, or expulsion of the IUD.
4. Sterilization
Contraception is an essential component of family planning, allowing individuals to control their reproductive choices and prevent unintended pregnancies. While there are various methods of contraception available, some people may choose to opt for a more permanent solution through sterilization. Sterilization of contraception, also known as surgical sterilization, is a highly effective and permanent method of birth control that involves blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes or vas deferens to prevent the release of eggs or sperm.
Types of Sterilization
There are two main types of sterilization procedures available for both men and women.
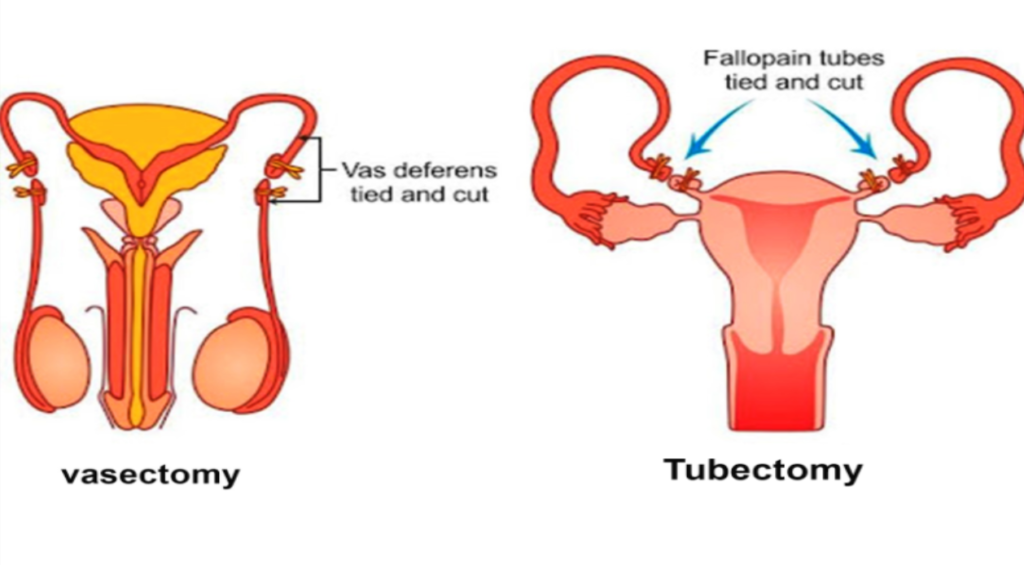
In women, tubal ligation is a common method where the fallopian tubes are either cut, tied, or sealed to prevent the eggs from reaching the uterus. This procedure is typically done through laparoscopic surgery and is considered to be a permanent method of contraception.
For men, vasectomy is the most common form of sterilization. During this procedure, the vas deferens, the tubes that carry sperm from the testicles, are cut or blocked to prevent the sperm from mixing with semen. Vasectomy is a simple and effective method of male contraception that is performed under local anesthesia in a doctor’s office.
Benefits of Sterilization
Sterilization of contraception offers several benefits to individuals seeking a permanent method of birth control. Firstly, it is highly effective in preventing pregnancy, with a success rate of over 99%. This reduces the need for other forms of contraception, such as pills or condoms, and provides long-term peace of mind.
Additionally, sterilization is a one-time procedure that does not require daily maintenance or follow-up appointments. Once the sterilization is done, there is no need to worry about unintended pregnancies or taking additional birth control measures. This can lead to improved sexual satisfaction and peace of mind for individuals and couples.
Considerations and Risks
While sterilization is a highly effective and permanent form of contraception, it is important to consider all factors before undergoing the procedure. Sterilization should be considered as a permanent decision, as reversal procedures are expensive and may not always be successful. Therefore, individuals should carefully weigh their options and discuss their decision with a healthcare provider.
Like any surgical procedure, sterilization does carry some risks, including the potential for infection, bleeding, or damage to surrounding organs. However, these risks are minimal, and the benefits of sterilization often outweigh the potential complications.
5. Natural Methods
Natural methods of contraception, also known as fertility awareness methods, involve tracking ovulation and avoiding unprotected sex during fertile periods. These methods, rely on understanding a woman’s menstrual cycle to determine when she is most fertile and when to avoid intercourse to prevent pregnancy·
Types of Natural Methods of Contraception
Calendar Method (Rhythm Method): This method involves tracking menstrual cycles over several months to predict fertile and non-fertile days· It requires abstaining from intercourse or using barrier methods during fertile days·
Lactational Amenorrhea Method (LAM): Exclusive breastfeeding can suppress ovulation and prevent pregnancy during the first six months postpartum if certain conditions are met, such as frequent breastfeeding day and night without any supplements·
Withdrawal Method (Pulling Out): Involves withdrawing the penis from the vagina before ejaculation to prevent sperm from entering the vagina· However, this method is less effective and not recommended as a primary contraceptive method·
Abstinence: Avoiding vaginal intercourse altogether during fertile days is a highly effective natural contraception method· Couples may engage in other sexual activities that do not involve vaginal penetration

FAQs:
1. Are barrier methods safe to use?
– Yes, barrier methods are safe to use when used correctly and consistently. They are also easily accessible and do not have any significant side effects.
2. Can barrier methods protect against all STIs?
– Barrier methods like condoms are effective in reducing the risk of most sexually transmitted infections. However, they may not provide complete protection against some infections like herpes and HPV.
3. Are barrier methods suitable for everyone?
– Barrier methods are suitable for most individuals, regardless of age or sexual orientation. It is essential to consult a healthcare provider to find the best method for your needs.
4. How long do barrier methods last?
– Barrier methods like condoms and diaphragms are typically meant for one-time use and should be disposed of after intercourse. Spermicides and contraceptive sponges may have varying durations of effectiveness.
5. Can barrier methods be used alongside other forms of contraception?
– Yes, barrier methods can be used in conjunction with other forms of contraception like hormonal birth control for added protection against pregnancy. It is essential to use them correctly to maximize their effectiveness.
6. What is the most effective method of contraception?
-The most effective method of contraception is considered to be long-acting reversible contraception (LARC), such as intrauterine devices (IUDs) and contraceptive implants· These methods are highly effective at preventing pregnancy and do not require daily or monthly attention once inserted·
7. Are hormonal methods of contraception safe for long-term use?
-Generally, hormonal methods of contraception, including birth control pills, patches, and hormonal IUDs, are considered safe for long-term use for most women· However, individual responses to hormonal contraception may vary, and it’s essential to discuss any concerns or medical history with a healthcare provider·
8.Can I switch between different methods of contraception?
-Yes, it is possible to switch between different methods of contraception based on individual preferences, lifestyle changes, or medical considerations· However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before making any changes to ensure a smooth transition and continued protection against pregnancy·
9.How do I know which contraception method is right for me?
-Choosing the right contraception method depends on various factors, including medical history, lifestyle, personal preferences, and individual health needs· A healthcare provider can help assess these factors and provide guidance on selecting the most suitable contraception method·
10.Are there any natural alternatives to hormonal contraception methods?
-Yes, there are natural alternatives to hormonal contraception methods, known as fertility awareness methods or natural family planning· These methods involve tracking menstrual cycles and fertility signs to identify fertile and non-fertile days· While natural methods can be effective when used correctly, they require diligent tracking and may not be as reliable as other forms of contraception· It’s essential to discuss the pros and cons of natural methods with a healthcare provider before choosing this option·
